AI algorithms on Turtle Bot
This is a 3 part project aimed at getting hands-on experience on each of the AI paradigms to learn using algorithms depending on the environments, agents, and tasks at hand.
I have used ROS melodic framework, which provides a virtual environment to test and visualize algorithms on robots (turtle bot in my case).
The environment can be configured to have changes in observability, stochasticity, and environment changes concerning change in time.
1. Part - 1: Search
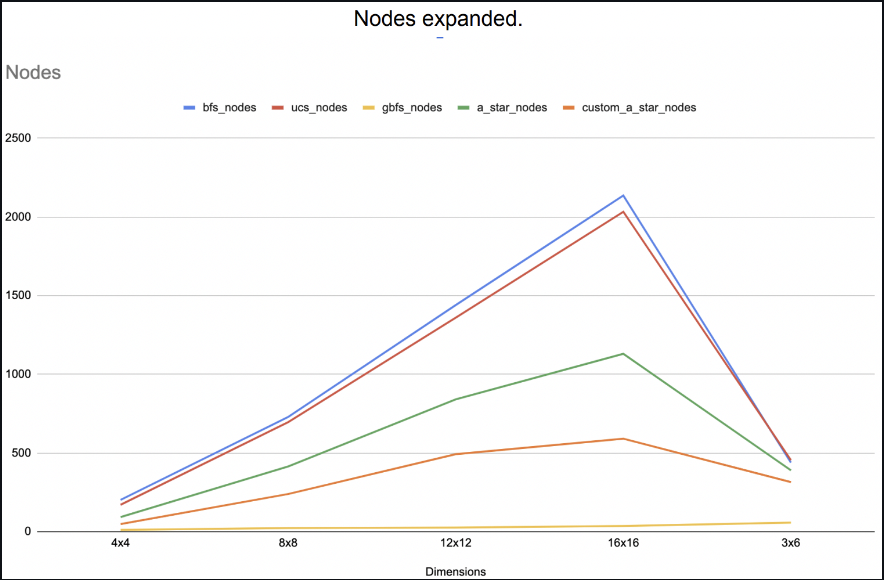
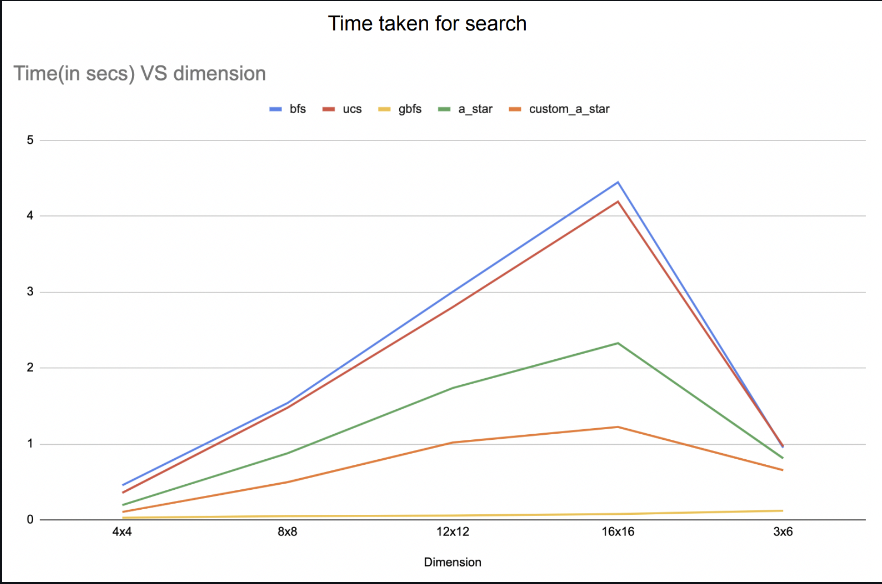
The environment is configured such that there are various obstacles at random locations, and there is a target that the turtle boot should reach from a random starting point. I evaluated search algorithms such as Breadth-First Search, Uniform Cost Search, Greedy Best First Search, and A-star (With manhattan and a variation of euclidean distance).
Evaluation of nodes expanded and time taken in each search for turtle bot to find the destination:
2. Part - 2: Planning
The environment chosen was bookWorld and cafeWorld and both worlds were find-pick-place with a size math criteria type of deterministic, fully observable, static environment.
In this part of the project, the development of common planning for both environments was defined using predicates, action, and goal states which reflects the state of both the state together.
The learning objective was to a. Define actions and goals generically so that solutions can be extended to multiple environments. b. Refining higher-level actions into lower-level bot understandable action set.
(PDDL files and code can be found in the repository.)
3. Part - 3: Reinforcement learning
The environment was configured such that it is partially observable, actions are stochastic and static.
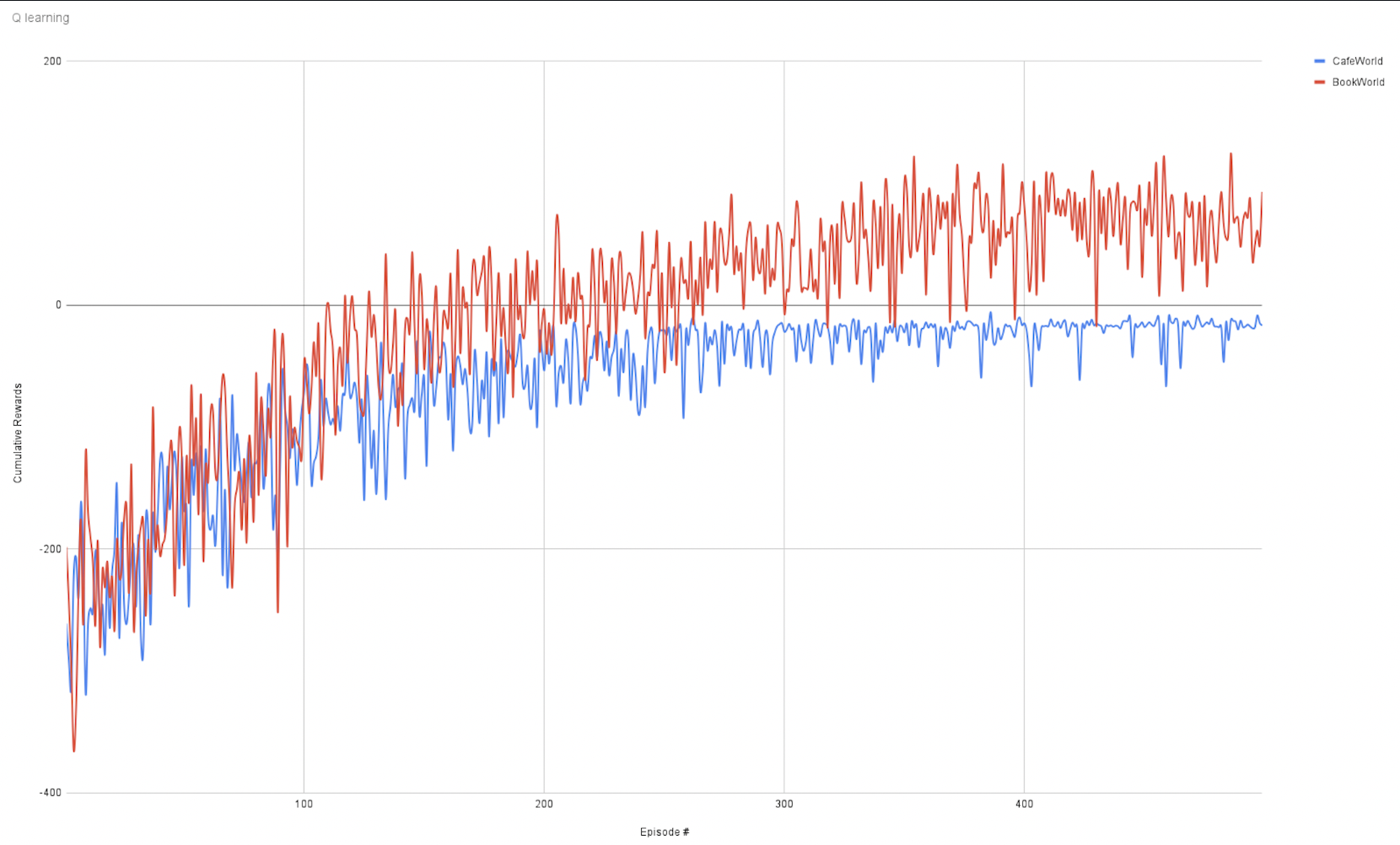
In this project, I have developed a program such that using a Q-learning algorithm, the program will give a set of optimal actions to be done in each belief state assumed by the robot. The environment also included reinforcement in terms of positive reward for successful execution of the action and negative reward for failure/ execution of invalid action. Furthermore, refinement of a higher-level action plan to a lower-level action plan using the best A-start search was added for maximum optimality.
The below graph shows the cumulative reward achieved for a particular episode during Q-learning by exploring the exploitation tradeoff on a logarithmic scale.